Unexpected roles of lipid kinases
Phospholipids are not mere structural components of animal cell membranes. Many of their metabolites are physiologically functional and are pivotal in intracellular signaling. Of those, diacylglycerol, or DAG, is a second messenger activating proteins containing a C1 domain, such as protein kinase C.
Evidence shows that phorbol esters, synthetic functional analogues of DAG, constitutively activate signal transduction pathways that lead to tumor formation. Thus, normal cells must regulate DAG levels within the physiological range. DAG kinases, or DGKs, are the key enzymes that regulate DAG levels. DGK phosphorylates DAG to phosphatidic acid, another lipid messenger molecule. DGKs are thought to be involved in the balanced control of these two lipid messenger signaling systems.
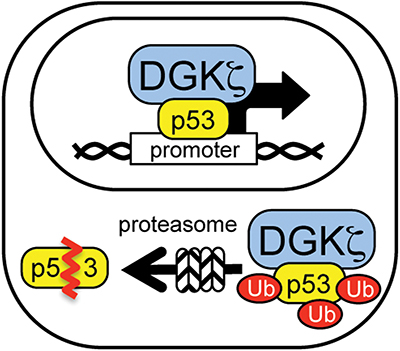 Functional implications of DGK-zeta in p53 regulation: Nuclear DGK-zeta modulates p53 transcriptional activity; cytoplasmic DGK-zeta facilitates p53 protein degradation.Courtesy of Kaoru Goto
Functional implications of DGK-zeta in p53 regulation: Nuclear DGK-zeta modulates p53 transcriptional activity; cytoplasmic DGK-zeta facilitates p53 protein degradation.Courtesy of Kaoru Goto
DGKs differ in their molecular structure, enzymatic activity, subcellular localization and binding partners. One DGK, DGK-zeta, contains both a nuclear localization signal and nuclear export signal (1), suggesting a shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Morphological studies on animal tissues report that DGK-zeta predominantly localizes to the nucleus in some cell types, while it exhibits both nuclear and cytoplasmic localization in others. from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in hippocampal neurons under stress conditions such as transient ischemia and seizures, and appears to be involved in stress responses.
What roles are assigned to DGK-zeta in the nucleus and the cytoplasm? Current data suggest that nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of DGK-zeta in neurons has a dual effect: While decreased levels of nuclear DGK-zeta lead to suppression of p53 transcriptional activity, increased levels of cytoplasmic DGK-zeta facilitate p53 protein degradation. reveal that DGK-zeta associates with p53, and DGK-zeta deletion suppresses p53 transcriptional activity under basal and DNA-damage conditions (2). DGK-zeta association with p53 facilitates cytoplasmic degradation of p53 through the ubiquitin proteasome system, or UPS. DGK-zeta deficiency, therefore, results in increased p53 levels. showed that DGK-zeta is degraded after cytoplasmic translocation in neurons, leading to increased levels of p53 protein and aberrant cell cycle reentry. In all, the levels of cytoplasmic DGK-zeta may serve as a supressor for p53 by facilitating its degradation, thus suppressing its cytotoxic effects.
What are the potential effects of DGK-zeta on other transcription factors? Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, or NF-kappaB, for example, is important in numerous biological processes, particularly immune response. showed that DGK-zeta knockdown enhances the NF-kappaB pathway in response to inflammatory cytokines. DGK-zeta downregulation accelerates phosphorylation of the p65 subunit and its nuclear translocation, increasing NF-kappaB transactivation activity. suggest that DGK-zeta exerts a regulatory effect on p53 and NF-kappaB (3).
A key question is determining the molecular mechanisms exerted by DGK-zeta on p53 and NF-kappaB. We want to know whether DGK-zeta catalytic activity, which alters the balance of DAG and phosphatidic acid in the nucleus and cytoplasm, is essential. How DGK activity modulates transcriptional activities is not known, but it turns out that p53 degradation mediated through cytoplasmic DGK-zeta and UPS is not kinase activity–dependent. unexpected roles of DGK-zeta on transcription factors; there is much to learn about how lipid-metabolizing enzymes impact cellular signaling involved in transcriptional regulation.
References
1. Goto, K. & Kondo, H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA.93, 11196-11201 (1996).
2. Tanaka, T. et al. J. Cell Sci.126, 2785-2797 (2013).
3. Tanaka, T. et al. Adv. Biol. Regul.60, 15-21 (2016).
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Bacterial enzyme catalyzes body odor compound formation
Researchers identify a skin-resident Staphylococcus hominis dipeptidase involved in creating sulfur-containing secretions. Read more about this recent Journal of Biological Chemistry paper.

Neurobiology of stress and substance use
MOSAIC scholar and proud Latino, Bryan Cruz of Scripps Research Institute studies the neurochemical origins of PTSD-related alcohol use using a multidisciplinary approach.

Pesticide disrupts neuronal potentiation
New research reveals how deltamethrin may disrupt brain development by altering the protein cargo of brain-derived extracellular vesicles. Read more about this recent Molecular & Cellular Proteomics article.

A look into the rice glycoproteome
Researchers mapped posttranslational modifications in Oryza sativa, revealing hundreds of alterations tied to key plant processes. Read more about this recent Molecular & Cellular Proteomics paper.

Proteomic variation in heart tissues
By tracking protein changes in stem cell‚Äďderived heart cells, researchers from Cedars-Sinai uncovered surprising diversity ‚ÄĒ including a potential new cell type ‚ÄĒ that could reshape how we study and treat heart disease.

Parsing plant pigment pathways
Erich Grotewold of Michigan State University, an ASBMB Breakthroughs speaker, discusses his work on the genetic regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis.


